Payment processing is a fundamental aspect of modern commerce, facilitating the transfer of funds between a customer and a merchant for goods or services rendered. Understanding the intricacies of payment processing can help businesses streamline operations, enhance security, and improve customer satisfaction.
The payment process begins when a customer initiates a transaction by selecting their preferred payment method (e.g., credit card, debit card, digital wallet) at the point of sale, whether it’s in-store, online, or via a mobile app.
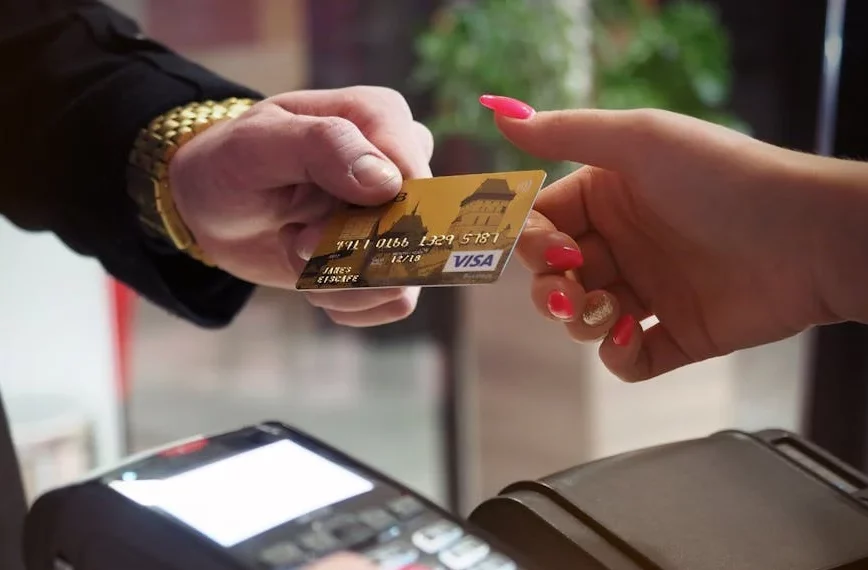
Upon receiving the payment details, the merchant sends an authorization request to the payment processor or acquiring bank. This request includes pertinent information such as the cardholder’s account number, transaction amount, and merchant identification.
The payment processor verifies the authenticity of the transaction by confirming the validity of the customer’s payment method and ensuring that sufficient funds are available. This step involves communication with the issuing bank, which evaluates the transaction based on various risk factors and security protocols.
Based on the authentication process, the issuing bank either approves or declines the transaction. If approved, the payment processor generates an authorization code, indicating that the funds can be transferred. In case of a decline, the customer is notified, and the transaction is terminated.
Once the transaction is authorized, the payment processor initiates the settlement process. Settlement involves transferring the funds from the customer’s account to the merchant’s account, typically within a few business days. This step may also include reconciliation of transactions and fees.
Upon successful settlement, both the customer and the merchant receive confirmation of the completed transaction. The customer may receive a receipt or confirmation email, while the merchant’s records are updated to reflect the incoming payment.
Throughout the payment process, various security measures are employed to safeguard sensitive information and prevent fraudulent activities. These measures may include encryption, tokenization, PCI DSS compliance, and advanced fraud detection algorithms.